RDC 982/2025 institutes a new model of health risk management and continuous compliance monitoring as a basis for granting, renewing, or canceling the Certificate of Good Manufacturing Practices (CBPF) and the Certificate of Good Distribution and/or Storage Practices (CBPDA).
This standard defines 17 objective criteria for evaluation and expands oversight mechanisms that can lead to inspections, investigations, and cancellation of certificates when there are substantial risks to public health.

What is RDC 982/2025, and why does it matter for your company?
RDC 982/2025 represents a paradigm shift in the way Anvisa evaluates establishments. With it, the agency changes from a purely documentary and episodic model to a continuous model, based on risk and evidence. The Resolution of the Collegiate Board also regulates the retroactive application in cases that have not yet had a decision published in the Official Gazette, which makes it essential to review petitions in progress.
This affects companies that want to have the Certificates of Good Manufacturing Practices (CBPF) and Distribution and/or Storage (CBPDA). The most impacted are companies that work with:
- manufacturing activities;
- distribution and storage of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API);
- drugs;
- Cannabis products for medicinal purposes;
- biological products;
- medical devices.
For executives and managers, this means that the certification will no longer be just a “seal” renewed periodically. This change makes it a dynamic process whose outcome depends on both the history of compliance and the continuous behavior of the company’s operation.
In practical terms, companies with weak controls will face a greater likelihood of scrutiny. On the other hand, organizations with robust governance and real-time monitoring gain predictability and a competitive advantage from this change.
The 17 criteria for health risk management applied to the granting or renewal of the CBPF or CBPD/A, according to the new RDC 982/2025, are:
- Product class and risk classification;
- Complexity and criticality of the establishment;
- Storage and transportation conditions of the input and/or finished product;
- History of compliance and regularity of the company and its products;
- History of compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Distribution/Storage by the establishment;
- Manufacturing line, process step, and pharmaceutical form to be certified;
- Post-market monitoring of products;
- Time elapsed since the last inspection;
- Inspection or GMP reports issued by Equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authority (AREE);
- Inspection or GMP reports issued by regulatory authorities or members of the PIC/S;
- Inspection reports issued by the health authorities of IMDRF countries
- Audit reports within the scope of the MDSAP;
- Results of laboratory, tax, or control analyses;
- National and international epidemiological and health context;
- Control through random inspection;
- Risk of discontinuation of products subject to health surveillance in the market
- Inspection reports are issued by Anvisa or state, district, or municipal Health Surveillance agencies.
What are the main changes in RDC 982/2025?
1. Health risk management as a central criterion
The rule formalizes the use of health risk management criteria for the evaluation of the concession and renewal of CBPF/CBPDA. In other words, Anvisa will combine technical information and risk indicators to decide whether a company will be certified or not. This makes it necessary for corporations to identify, measure, and evidence their health risks continuously, not just at the time of punctual audits.
2. List of criteria
The text of the RDC specifies a set of criteria that must be evaluated in a combined manner to stipulate the health risk of the establishment. These criteria add operational elements, non-compliance histories, nature of the products, complexity of the processes, and external factors, among others.
3. Continuous monitoring and action mechanisms
In addition to the initial assessment, Anvisa starts to practice continuous monitoring of compliance. This means that alerts, reports, adverse event notifications, investigations, and inspections can be triggered throughout the certificate’s validity period. In addition, RDC 982/2025 also allows the cancellation of the certificate if the technical opinion points to any serious compliance.
4. Recognition of foreign authorities and regulatory trust practices
The resolution provides, when applicable, for the use of information from Equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities (AREE) as input for evaluation. This change makes it possible to speed up processes when there is mutual regulatory trust; however, at the same time, it requires companies to know what documentation and international history can be considered by Anvisa.
5. Regulation on the use of AI for health risk management
RDC 982/2025 is directly related to Artificial Intelligence (AI). In Chapter II, Article 3, paragraph 3, Anvisa establishes that AI models can be used in the health risk management process for granting or renewing the CBPF and CBPDA.
However, the use of AI is not unrestricted. The rule determines that any model adopted must:
- Ensure technical consistency in the analysis;
- Protect sensitive data, complying with the LGPD;
- Ensure traceability of the information and decisions generated;
- Undergo validation by Anvisa before entering official use.
In practice, this means that AI can support the integrated assessment of the 17 risk criteria listed in the resolution, helping to identify patterns, predict non-conformities, and optimize the inspection process. But ultimate responsibility and oversight remain with Anvisa, preventing critical decisions from being made without human control.
Some of the examples of the use of AI in health risk management in compliance with the DRC are:
- Predictive risk analysis based on compliance history – AI can cross-reference internal company data (past audits, non-conformities, production deviations, among others) with external data from health authorities to predict the probability of failure in future inspections. This allows you to take corrective actions in advance so that non-conformities that occurred in the past do not come to a minimum.
- Automated monitoring of storage and transportation conditions – Sensors with the Internet of Things (IoT) can collect temperature, humidity, and vibration data in real time, and AI models analyze deviations and trends in this information. By identifying patterns that precede non-conformities, the company can act before there is an impact on the product/service.
- Correlation of market data with epidemiological context – Artificial Intelligence can integrate international alerts and local data from outbreaks or recalls to adjust production and inspection plans, and thus helps to prioritize critical batches and reinforce traceability.
- Intelligent risk classification by product and manufacturing line – Machine learning models can classify and rank products, processes, and industrial plants based on criticality, pharmaceutical form, and facility complexity. This allows the quality team to focus resources and inspection efforts on the most sensitive areas.

What are the practical impacts of this Resolution of the Collegiate Board?
As you can imagine, RDC 982/2025 reflects several changes and adaptations for companies that want to maintain/earn their certificates or just ensure an operation in compliance with the best sanitary practices in the market.
The main impacts of the resolution can be divided into three categories: operational, financial, and reputational & business. Learn more about each of them below!
Operational impact
- Continuity of controls: With the implementation of Collegiate Board Resolution 982/2025, companies will have real-time indicators (or with a frequent cadence) that show production performance, deviations, non-conformities, and effectiveness of CAPAs.
- Integration between areas: Regulation, Quality, Supply Chain and IT sectors start to work in an integrated way to demonstrate end-to-end control of compliance with the resolution.
Financial impact
- Adequacy costs: It is necessary to increase investments in quality management systems. Relying on automation solutions, internal audits, and training may be necessary.
- Risk of lost revenue: In the event of non-compliance, certificate cancellation or the need for corrective requirements that disrupt operations can lead to direct losses and remediation costs.
- Market benefit: On the other hand, companies with evidence of governance and ongoing compliance tend to shave time off future regulatory processes and potentially gain access to markets that value that compliance.
Reputational and business impact
- Market exposure: Any punitive measures (such as investigations or the suspension of certificates) indicated by RDC 982/2025 in case of non-compliance have a direct impact on the confidence of partners, customers, and investors.
- Competitive differentiation: Operating with transparent compliance metrics can be an advantage in contracts with demanding stakeholders in relation to health safety, as well as several players in the international market.

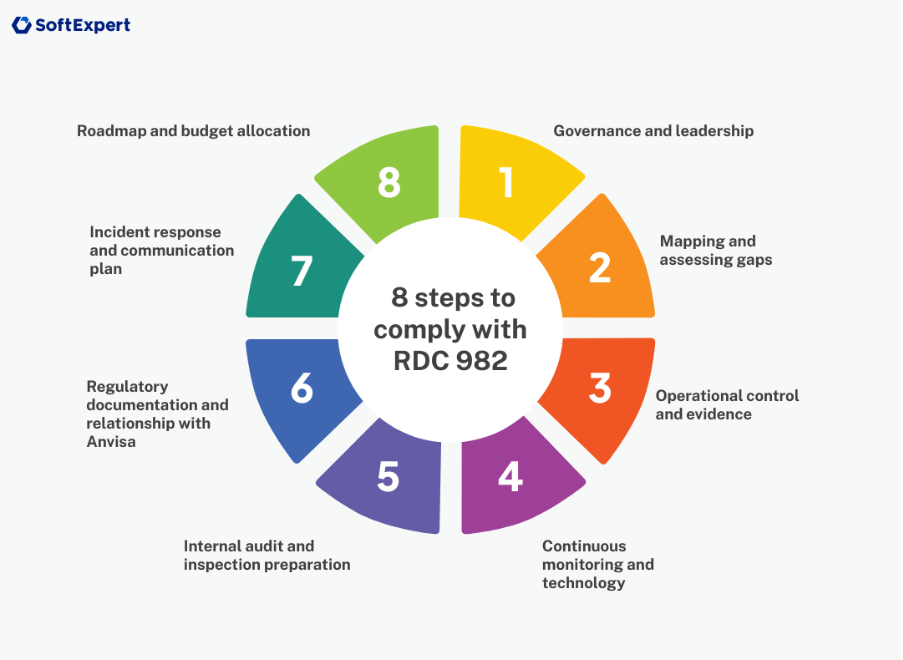
8 steps for your company to adapt to the new RDC
To prevent the negative impacts of Collegiate Board Resolution 982/2025 from affecting your company, it is essential to know how to adapt your operation and ensure compliance with the main requirements of the RDC. This means reviewing internal policies, stipulating ongoing controls, implementing changes in a structured way, and more.
To facilitate this adaptation, we have prepared a brief checklist that suits most of the profiles of companies affected by the new resolution. But remember this is just a standard structure; adapt everything to your company’s reality and use the information as a starting point.
1. Governance and leadership
- Appoint a lead project officer for the adaptation to the DRC. This person must have the authority to direct resources (financial, time, personnel, among others.
- Create a multidisciplinary committee (involving sectors such as Regulation, Quality, Supply Chain, IT, Legal, among others) and organize periodic meetings to monitor the KPIs related to the project – which will be defined later in this checklist.
2. Mapping and evaluating gaps
- Perform a gap analysis considering the 17 criteria mentioned in the RDC. At this point, try to map the presence or absence of controls, documentary evidence, indicators, residual risks, and other criteria.
- Then, prioritize the order of resolution of the gaps found, using as the main criterion the impact of each one on compliance with the RDC. Rate this impact by taking into account the level of risk (high, medium, low) versus the ease of mitigation of each.
3. Operational control and evidence
- Consolidate all the evidence found in the previous processes. These can be procedures, production records, calibration reports, traceability, deviation reports, and CAPAs.
- Implement key indicators (KPIs) that will serve as the basis for evaluating the DRC compliance project. For example, you can use the frequency of critical deviations per batch, the average CAPA closing time, the average storage temperature, the compliance level, and more.
4. Continuous monitoring and technology
- Adopt a digital QMS system that allows you to collect and query evidence in real time. Also, prioritize those solutions that have integrations with manufacturing and storage systems (MES, WMS) or that already have these tools among their resources.
- Implement dashboards that show the level of compliance and automatic alerts for critical levels of non-compliance.
5. Internal audit and preparation for inspection
- Plan a cycle of internal audits focused on the 17 criteria, using standardized checklists and other tools that increase the chances of success in an audit.
- Simulate inspections and review responses and evidence found in that simulation.
6. Regulatory documentation and relationship with Anvisa
- Review petitions and dossiers in progress to verify the impact of the rule on your company, especially in cases without a decision published in the Official Gazette of the Union (DOU).
- Establish a communication flow with the technical/regulatory area to send proactive evidence when requested.
7. Incident response and communication plan
- Set a response playbook for these occasions. Remember to include actions aimed at investigation, mitigation, internal reporting, and external communication (with customers and health authorities, when necessary).
- Train teams to ensure agile turnaround time and the quality of evidence.
8. Roadmap and budget allocation
- Set up a timeline for the planning and execution of all previous activities. Also, create clear milestones/deadlines for each one, such as what will be done from 0 to 3 months, from 3 to 9 months, and finally, from 9 to 18 months. Also, include who will be the people responsible for each of these steps.
- Budget for all critical initiatives, including investment in tools, systems, regulatory consulting, capacity building, etc.
The ideal solution for companies adapted by RDC 982/2025
Adapting to the new RDC and having a defined framework to analyze gaps, plan actions, and adapt your operation is not enough to facilitate compliance with the new RDC. Companies that want to make this process more agile, secure, and automated need to go further: rely on a compliance and quality management system such as SoftExpert Suite.
With this system, you can perform a series of tasks that help your company comply with Anvisa regulations. Among them are continuous compliance monitoring, full process traceability, integrated AI validated by Anvisa standards, automation of change and non-compliance management, predictive risk analysis, and much more.
Find out more about how SoftExpert Suite already has RDC 982/2025-ready features.
Continuous monitoring of compliance with the Collegiate Board Resolution
SoftExpert QMS automates and integrates essential quality management processes, such as planning, audits, quality control, nonconformities, documents, suppliers, risks and indicators. This reduces rework, increases standardization, and strengthens compliance.
This allows the system to identify trends in non-compliance before they become problems for your business. In addition, you have real-time alerts and dashboards to speed up strategic decision-making, mitigating negative impacts.
This is how the company Pharlab automated the management of training and documents, reducing quality management costs by 48%.
Automatic preparation for DRC audits
With the Audit functionality, you can manage your audits from planning to preparation and execution, setting schedules, developing plans, and issuing reports efficiently.
This allows you to automatically organize evidence according to each criterion of RDC 982/2025, as well as generate structured reports for Anvisa’s auditors – and all this with full traceability of each step of the audit process.
Intelligent management changes
A series of resources work in an integrated way to ensure intelligent and automated management of the various changes (and controls of such changes) that the new RDC can generate in your company’s operation.
By combining tools such as Workflow, Document, and Training it is possible to:
- Generate automated flows that ensure proper approval/review of documents;
- Share these documents with different areas/people and manage access to them;
- Automatically make available all mandatory training related to RDC 982.
In this way, the pharmaceutical company União Química was able to digitize more than three thousand critical documents, which generated a 30% increase in productivity thanks to instant access to the information in these documents.
Predictive risk analysis
Using Copilot AI and Risk functionality, you use the analytics power of artificial intelligence with the ability to document, simulate, and remediate compliance risks.
Copilot AI identifies patterns that can cause non-conformities and, in addition, offers automatic recommendations for preventive and corrective actions. Using the Risk tool, you can simulate different scenarios and thus make the right decision to deal with these threats.

Conclusion
RDC 982/2025 represents a milestone in the way Anvisa conducts health risk management, bringing more technical rigor, transparency, and predictability to the process of granting and renewing certifications. By aligning evaluation criteria with international practices and incorporating technological resources, the resolution reinforces the need for companies to adopt robust compliance management systems capable of responding quickly to increasingly dynamic regulatory requirements.
For manufacturers, importers, and distributors of APIs, medicines, biologics, medical devices, and medical cannabis derivatives, compliance with these requirements goes beyond legal compliance. The new standard is a mechanism to maintain competitiveness, protect reputation and ensure business continuity in a highly regulated market. Therefore, anticipating changes and investing in continuous improvement processes will be essential to transform the obligations of RDC 982/2025 into a strategic advantage.
If your organization operates with these products, now is the time to:
- Start a gap analysis focused on the 17 criteria of the resolution;
- Prioritize the implementation of continuous monitoring with actionable indicators;
- Engage senior leadership to ensure the necessary resources and governance.
Looking for more efficiency and compliance in your operations? Our experts can help identify the best strategies for your company with SoftExpert solutions. Contact us today!
FAQ about RDC 982/2025
Yes, the resolution entered into force on the date of its publication in the Official Gazette. Companies should consider the rule for lawsuits that have not yet been published.
As the RDC has been in force since July 29, 2025, the adaptation must be immediate for new processes.
Seek to use robust APIs that allow integration with ERPs and legacy systems without interruption.
APIs, medicines, medical cannabis products, biologics, and medical devices are explicitly listed in the scope.
Distributors and warehousers are now evaluated by the same risk management framework. Additionally, the evidence of quality control and traceability gains relevance in maintaining the CBPDA.
Yes, the standard provides for continuous monitoring, and a technical opinion based on risk management may result in administrative measures, including the suspension or cancellation of certificates when relevant risks are identified.
Some of the evidence required will be the complete compliance history, continuous monitoring data, and documented risk analyses.
Through an integrated QMS, compliance KPIs, regular internal audits, auditable electronic records, and the ability to respond quickly to deviations and investigations.
Current certifications remain valid but are subject to ongoing monitoring and possible cancellation based on risk analysis.
Among the main ones are the loss of certifications, fines, interruption of operations and loss of competitiveness.
To find out this, evaluate whether your AI tool meets the standards of consistency, data protection, traceability, and technical validation required by Anvisa.